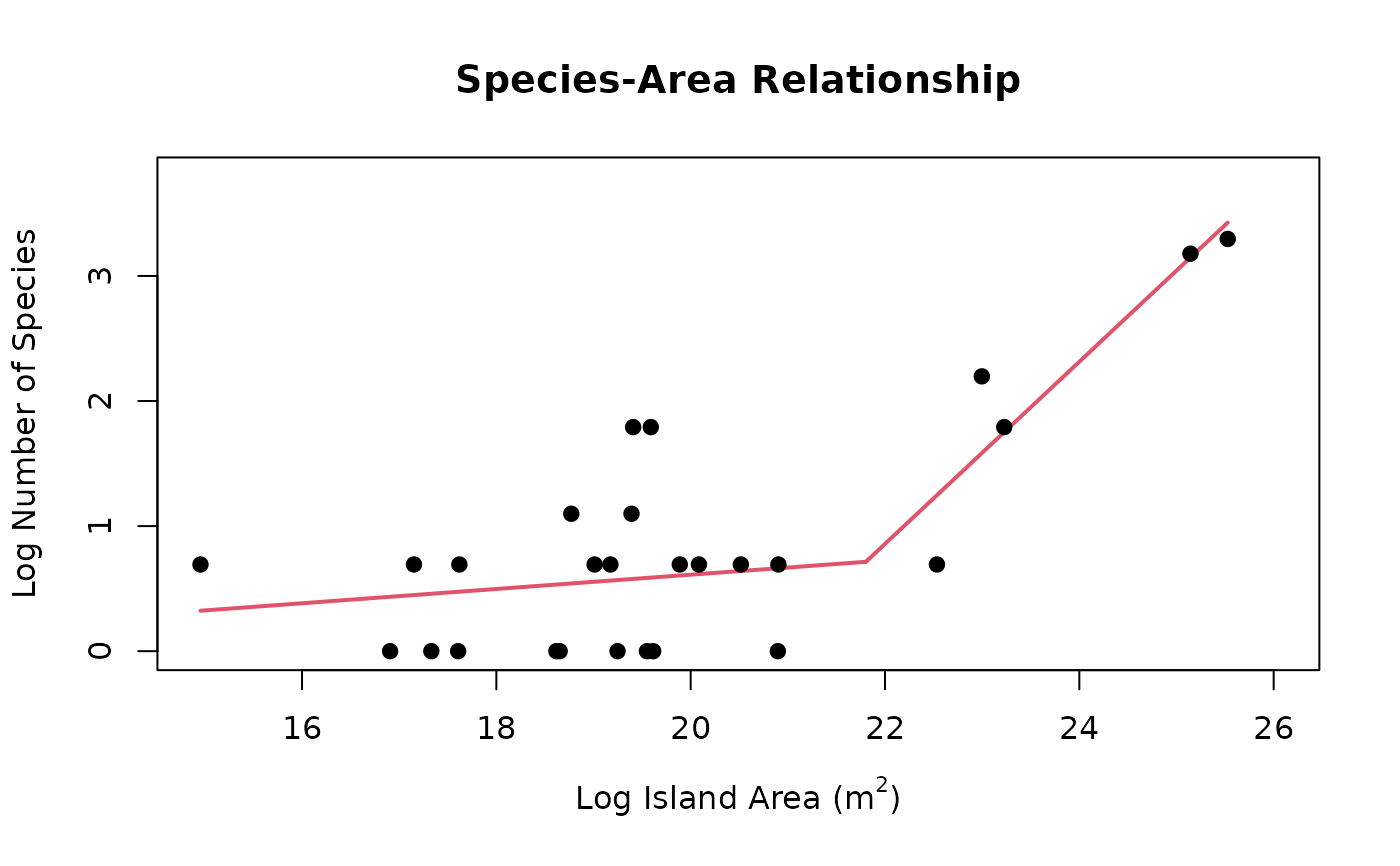
Use segmented regression to create a species-area relationship (SAR) plot. The X axis represents log(island area) and the Y axis represents log(number of species)
Usage
create_sar(occurrences, npsi = 1, visualize = FALSE)
create_SAR(occurrences, npsi = 1, visualize = FALSE)Arguments
- occurrences
The dataframe output by
ssarp::find_areas()(or if using a custom dataframe, ensure that it has the following columns: specificEpithet, areas)- npsi
The maximum number of breakpoints to estimate for model selection. Default: 1
- visualize
(boolean) Whether the plot should be displayed when the function is called. Default: FALSE
Value
A list of class SAR with 5 items including:
summary: the summary outputsegObjorlinObj: the regression object (segObjwhen segmented,linObjwhen linear)aggDF: the aggregated dataframe used to create the plotAICscores: the AIC scores generated during model selectionAllModels: a list of models created in model selection, labeled by number of breakpoints
Details
If the user would prefer to create their own plot of the
ssarp::create_sar() output, the aggDF element of the returned list
includes the raw points from the plot created here. They can be accessed
as demonstrated in the Examples section.
Examples
# The GBIF key for the Anolis genus is 8782549
# Read in example dataset filtered from:
# dat <- rgbif::occ_search(taxonKey = 8782549,
# hasCoordinate = TRUE,
# limit = 10000)
dat <- read.csv(system.file("extdata",
"ssarp_Example_Dat.csv",
package = "ssarp"))
land <- find_land(occurrences = dat)
areas <- find_areas(occs = land)
#> ℹ Recording island names...
#> ℹ Assembling island dictionary...
#> ℹ Adding areas to final dataframe...
seg <- create_sar(occurrences = areas,
npsi = 1,
visualize = FALSE)
plot(seg)
 summary <- seg$summary
model_object <- seg$segObj
points <- seg$aggDF
summary <- seg$summary
model_object <- seg$segObj
points <- seg$aggDF
