This function converts an input sf to an
sf object with H3 hexagons.
It requires the h3r package to be installed.
Details
Non-polygon x will be converted to polygons using
sf::st_concave_hull. If the input is not convertible
to polygons, the function will throw an error.
Examples
lastpar <- par(mfrow = c(1, 1))
library(sf)
if (rlang::is_installed("h3r")) {
library(h3r)
options(sf_use_s2 = FALSE)
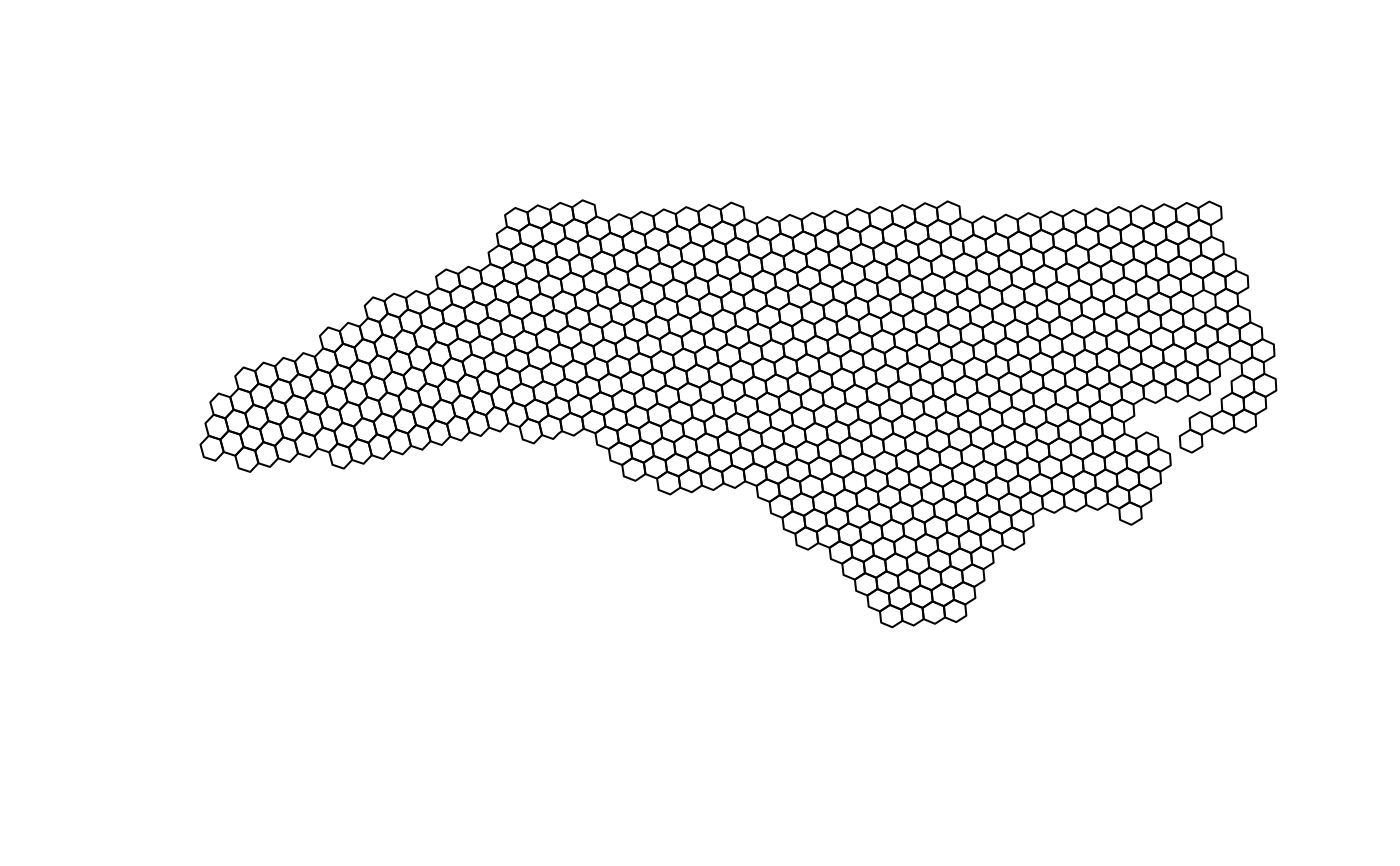
ncpath <- system.file("shape/nc.shp", package = "sf")
nc <- read_sf(ncpath)
nc <- st_transform(nc, "EPSG:4326")
# note that it will throw a warning if
# the input is MULTIPOLYGON.
nc_comp_region_h3 <-
suppressWarnings(
par_make_h3(
nc,
res = 5L
)
)
plot(sf::st_geometry(nc_comp_region_h3))
}
#> Loading required package: h3lib
#>
#> Attaching package: ‘h3r’
#> The following object is masked from ‘package:terra’:
#>
#> gridDistance
#> Input sf object should be in WGS84 (EPSG:4326) CRS.
#> although coordinates are longitude/latitude, st_intersects assumes that they
#> are planar
 par(lastpar)
par(lastpar)