All the tests were done on an Arch Linux x86_64 machine with an Intel(R) Core(TM) i7 CPU (1.90GHz).
Empirical likelihood computation
We show the performance of computing empirical likelihood with
el_mean(). We test the computation speed with simulated
data sets in two different settings: 1) the number of observations
increases with the number of parameters fixed, and 2) the number of
parameters increases with the number of observations fixed.
Increasing the number of observations
We fix the number of parameters at
,
and simulate the parameter value and
matrices using rnorm(). In order to ensure convergence with
a large
,
we set a large threshold value using el_control().
library(ggplot2)
library(microbenchmark)
set.seed(3175775)
p <- 10
par <- rnorm(p, sd = 0.1)
ctrl <- el_control(th = 1e+10)
result <- microbenchmark(
n1e2 = el_mean(matrix(rnorm(100 * p), ncol = p), par = par, control = ctrl),
n1e3 = el_mean(matrix(rnorm(1000 * p), ncol = p), par = par, control = ctrl),
n1e4 = el_mean(matrix(rnorm(10000 * p), ncol = p), par = par, control = ctrl),
n1e5 = el_mean(matrix(rnorm(100000 * p), ncol = p), par = par, control = ctrl)
)Below are the results:
result
#> Unit: microseconds
#> expr min lq mean median uq max
#> n1e2 447.205 486.254 525.1408 505.1695 573.3065 639.906
#> n1e3 1242.714 1408.559 1532.4583 1507.2885 1626.6765 2582.548
#> n1e4 10847.710 12445.111 14628.1767 15071.0550 16124.2235 19346.727
#> n1e5 173354.969 202472.709 242520.7464 234432.1965 259868.0575 400198.154
#> neval cld
#> 100 a
#> 100 a
#> 100 b
#> 100 c
autoplot(result)
#> Warning: `aes_string()` was deprecated in ggplot2 3.0.0.
#> ℹ Please use tidy evaluation idioms with `aes()`.
#> ℹ See also `vignette("ggplot2-in-packages")` for more information.
#> ℹ The deprecated feature was likely used in the microbenchmark package.
#> Please report the issue at
#> <https://github.com/joshuaulrich/microbenchmark/issues/>.
#> This warning is displayed once per session.
#> Call `lifecycle::last_lifecycle_warnings()` to see where this warning was
#> generated.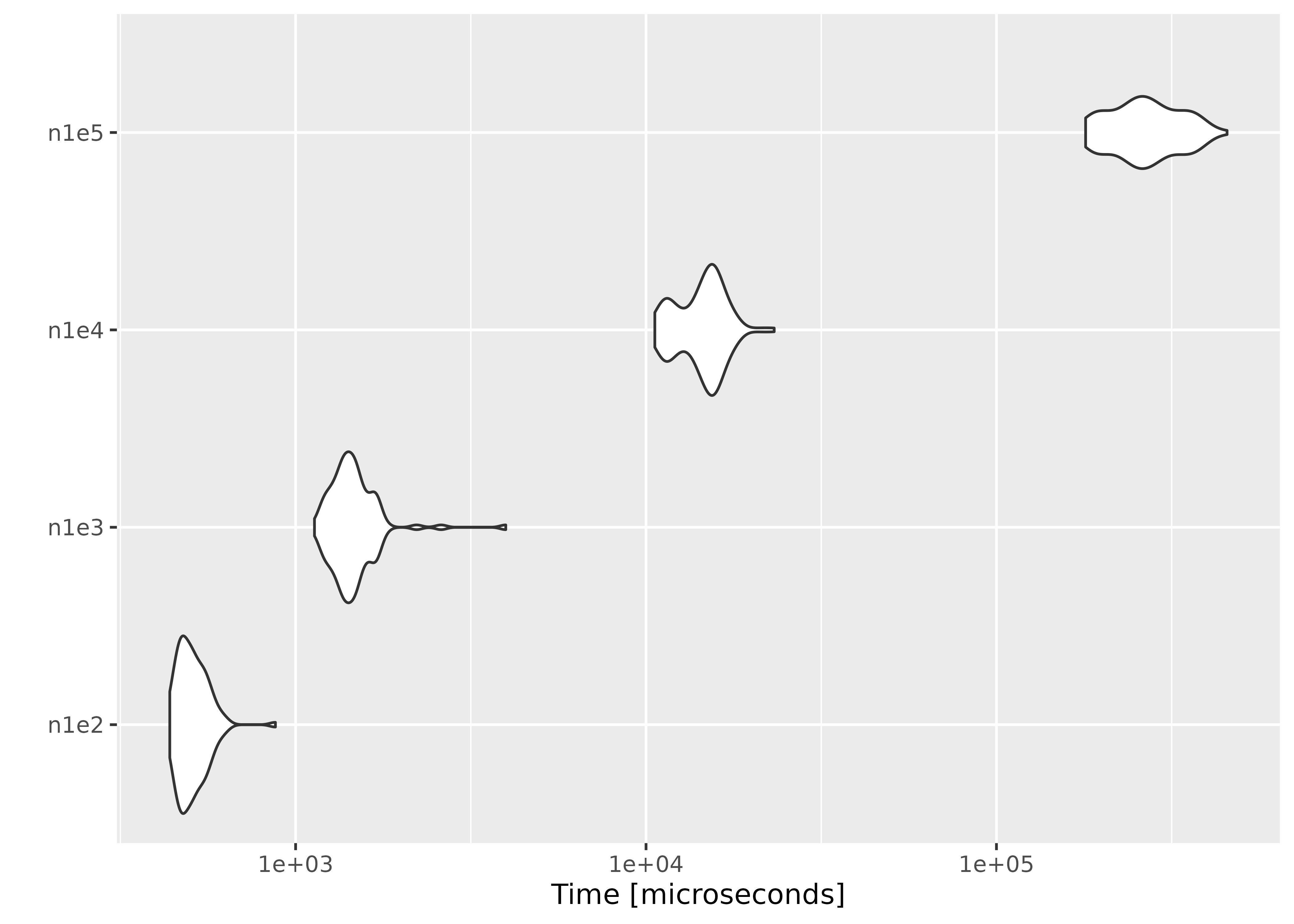
Increasing the number of parameters
This time we fix the number of observations at , and evaluate empirical likelihood at zero vectors of different sizes.
n <- 1000
result2 <- microbenchmark(
p5 = el_mean(matrix(rnorm(n * 5), ncol = 5),
par = rep(0, 5),
control = ctrl
),
p25 = el_mean(matrix(rnorm(n * 25), ncol = 25),
par = rep(0, 25),
control = ctrl
),
p100 = el_mean(matrix(rnorm(n * 100), ncol = 100),
par = rep(0, 100),
control = ctrl
),
p400 = el_mean(matrix(rnorm(n * 400), ncol = 400),
par = rep(0, 400),
control = ctrl
)
)
result2
#> Unit: microseconds
#> expr min lq mean median uq max
#> p5 725.847 767.1845 820.8142 802.1845 846.7885 1482.451
#> p25 2895.253 2949.8145 3049.8471 2983.7680 3047.2170 6089.104
#> p100 23415.755 25950.9240 28376.1969 26387.1750 30999.7225 49459.272
#> p400 268970.349 292313.7685 327537.1182 315001.4870 341523.3385 531163.398
#> neval cld
#> 100 a
#> 100 a
#> 100 b
#> 100 c
autoplot(result2)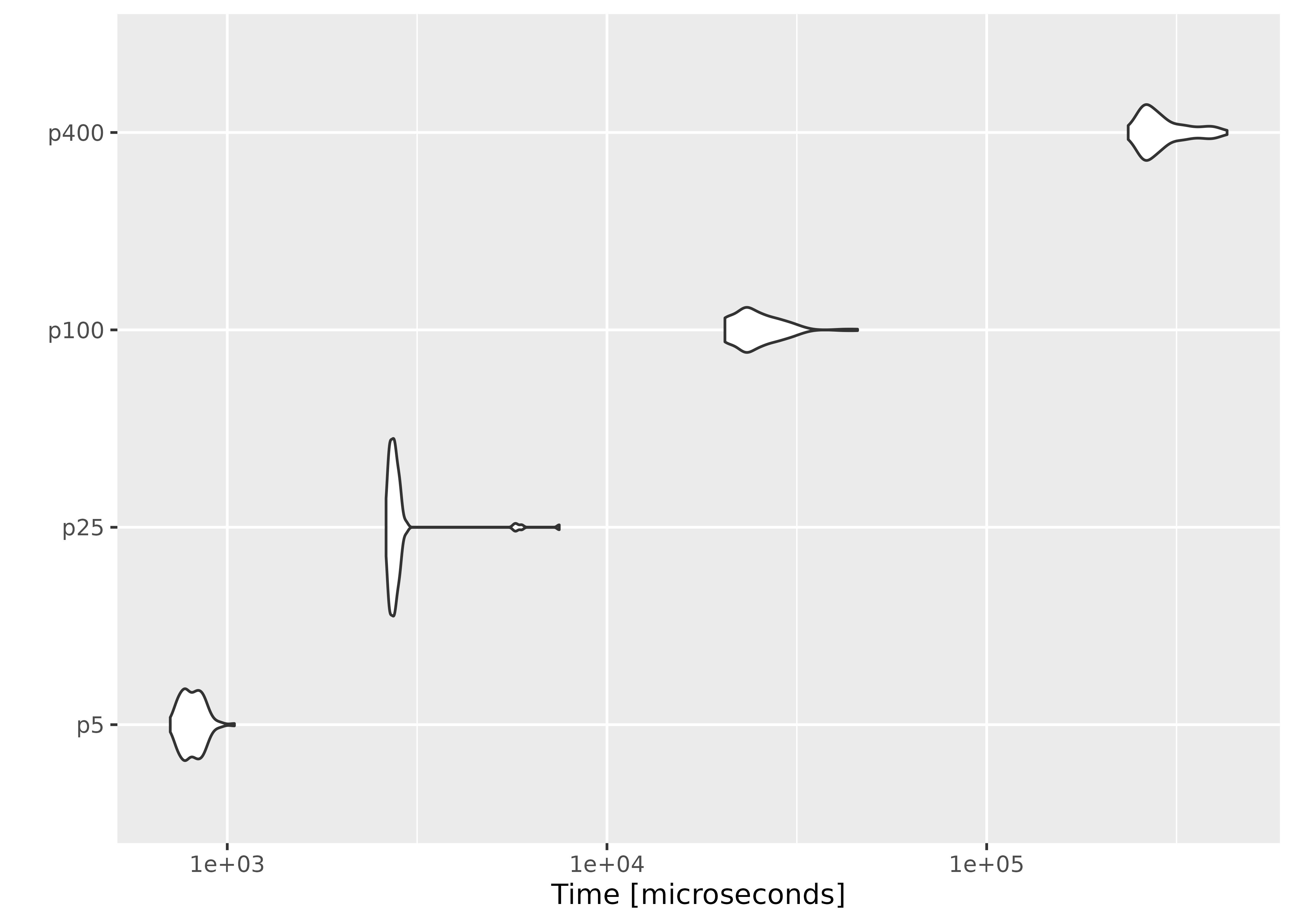
On average, evaluating empirical likelihood with a 100000×10 or 1000×400 matrix at a parameter value satisfying the convex hull constraint takes less than a second.
