Takes a geographic object or bounding box as an input and outputs a bounding box, represented as a bounding box, corner points or rectangular polygon.
Usage
geo_bb(
shp,
scale_factor = 1,
distance = 0,
output = c("polygon", "points", "bb")
)Arguments
- shp
Spatial object
- scale_factor
Numeric vector determining how much the bounding box will grow or shrink. Two numbers refer to extending the bounding box in x and y dimensions, respectively. If the value is 1, the output size will be the same as the input.
- distance
Distance in metres to extend the bounding box by
- output
Type of object returned (polygon by default)
See also
bb_scale
Other geo:
bbox_scale(),
bind_sf(),
geo_bb_matrix(),
geo_buffer(),
geo_length(),
geo_projected(),
geo_select_aeq(),
quadrant()
Examples
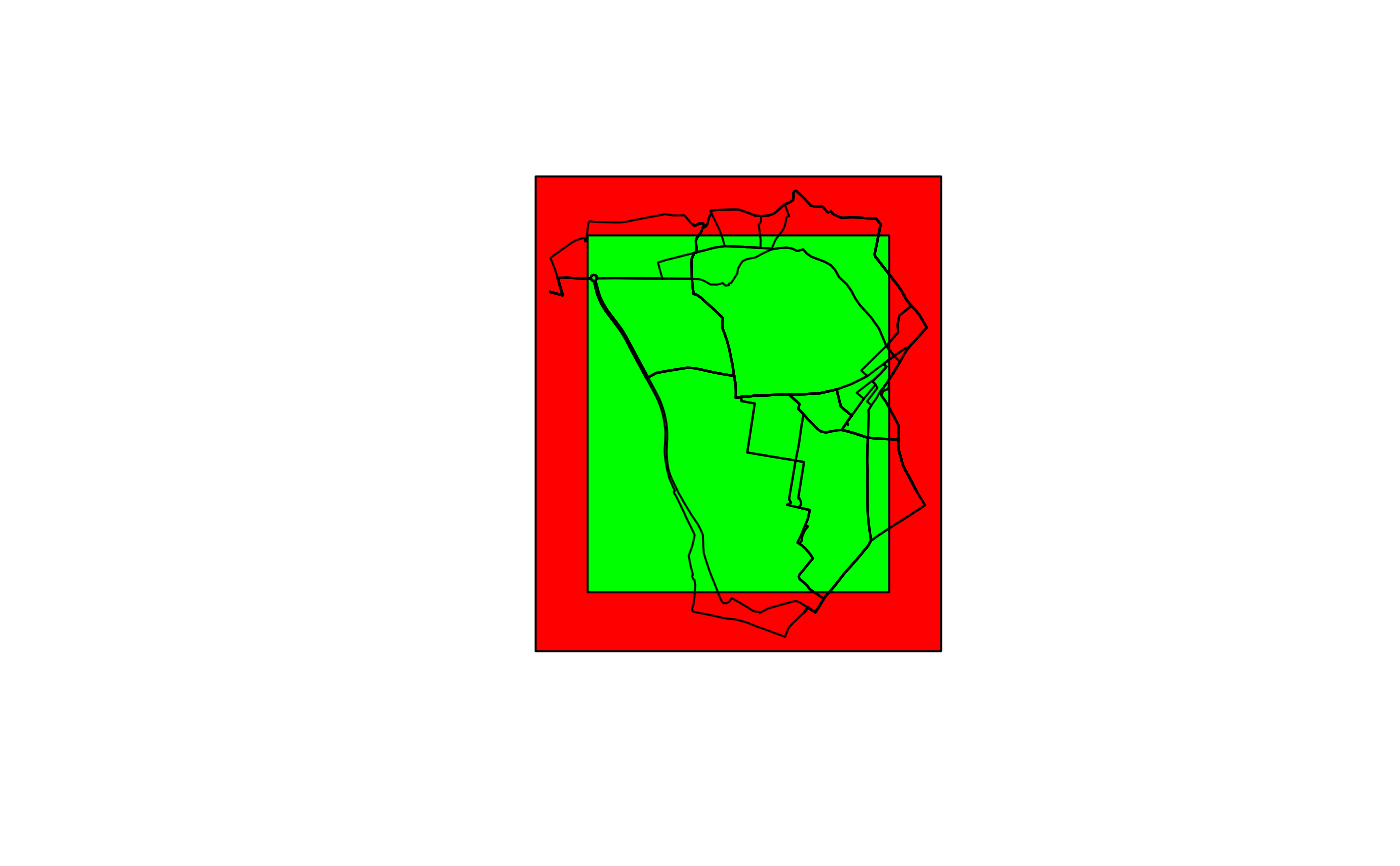
shp <- routes_fast_sf
shp_bb <- geo_bb(shp, distance = 100)
plot(shp_bb, col = "red", reset = FALSE)
plot(geo_bb(routes_fast_sf, scale_factor = 0.8), col = "green", add = TRUE)
plot(routes_fast_sf$geometry, add = TRUE)
 geo_bb(shp, output = "point")
#> Geometry set for 4 features
#> Geometry type: POINT
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: -1.550964 ymin: 53.80248 xmax: -1.510987 ymax: 53.83041
#> Geodetic CRS: WGS 84
#> POINT (-1.550964 53.80248)
#> POINT (-1.510987 53.80248)
#> POINT (-1.510987 53.83041)
#> POINT (-1.550964 53.83041)
geo_bb(shp, output = "point")
#> Geometry set for 4 features
#> Geometry type: POINT
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: -1.550964 ymin: 53.80248 xmax: -1.510987 ymax: 53.83041
#> Geodetic CRS: WGS 84
#> POINT (-1.550964 53.80248)
#> POINT (-1.510987 53.80248)
#> POINT (-1.510987 53.83041)
#> POINT (-1.550964 53.83041)