This function assigns linestring features, many of which in an
sf object can form route networks, into groups.
By default, the function igraph::clusters() is used to determine
group membership, but any igraph::cluster*() function can be used.
See examples and the web page
igraph.org/r/doc/communities.html
for more information. From that web page, the following clustering
functions are available:
Arguments
- rnet
An sf, sfc, or sfNetwork object representing a route network.
- ...
Arguments passed to other methods.
- cluster_fun
The clustering function to use. Various clustering functions are available in the
igraphpackage. Default:igraph::clusters().- d
Optional distance variable used to classify segments that are close (within a certain distance specified by
d) to each other but not necessarily touching- as.undirected
Coerce the graph created internally into an undirected graph with
igraph::as.undirected()? TRUE by default, which enables use of a wider range of clutering functions.
Value
If the input rnet is an sf/sfc object, it returns an integer vector reporting the groups of each network element. If the input is an sfNetwork object, it returns an sfNetwork object with an extra column called rnet_group representing the groups of each network element. In the latter case, the connectivity of the spatial object is derived from the sfNetwork object.
Details
cluster_edge_betweenness, cluster_fast_greedy, cluster_label_prop,
cluster_leading_eigen, cluster_louvain, cluster_optimal, cluster_spinglass, cluster_walktrap
Note
These functions rely on the igraph package. If igraph is not installed, the function will return a message.
See also
Other rnet:
gsection(),
islines(),
overline(),
rnet_breakup_vertices()
Examples
if (requireNamespace("igraph", quietly = TRUE)) {
rnet <- rnet_breakup_vertices(stplanr::osm_net_example)
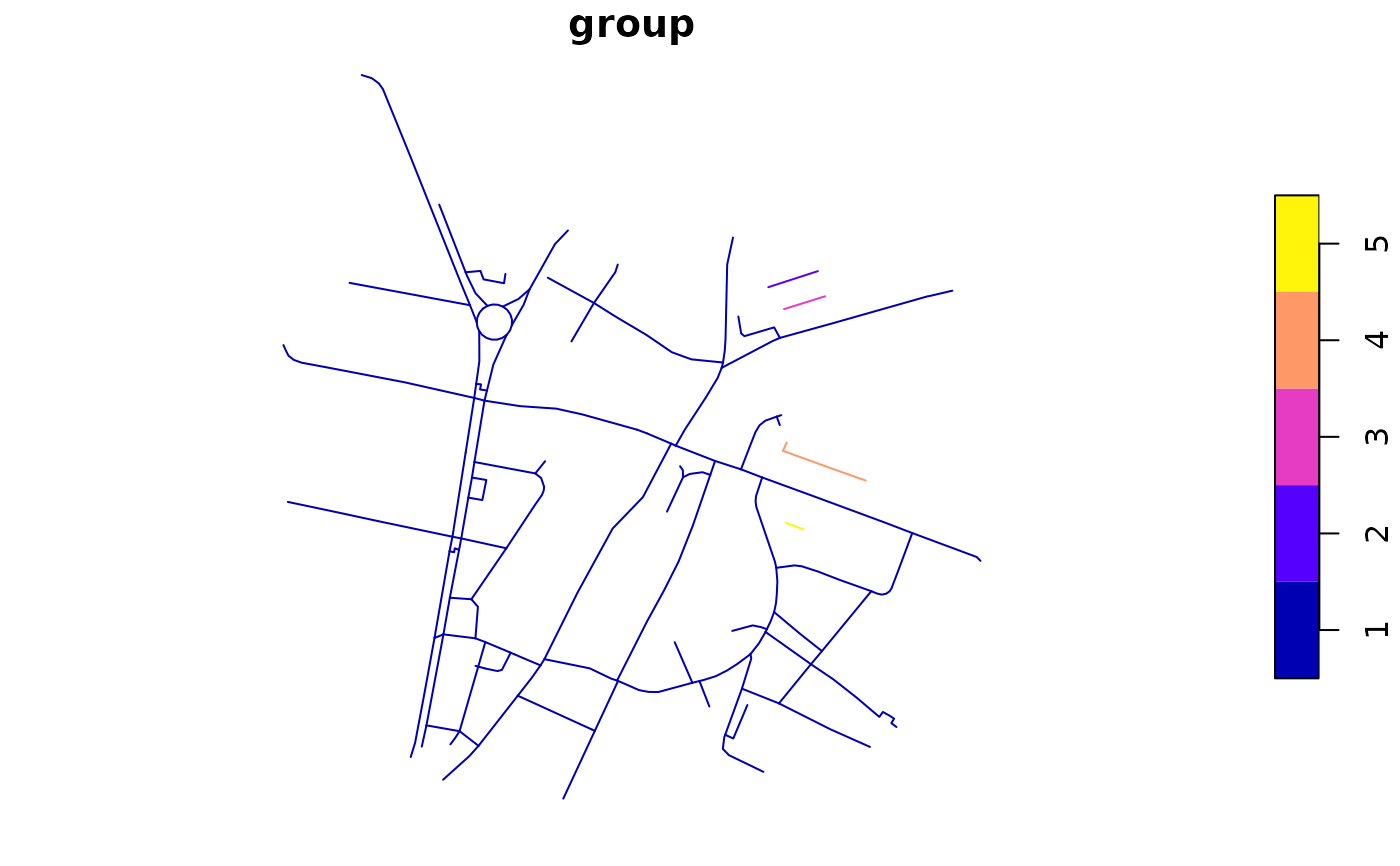
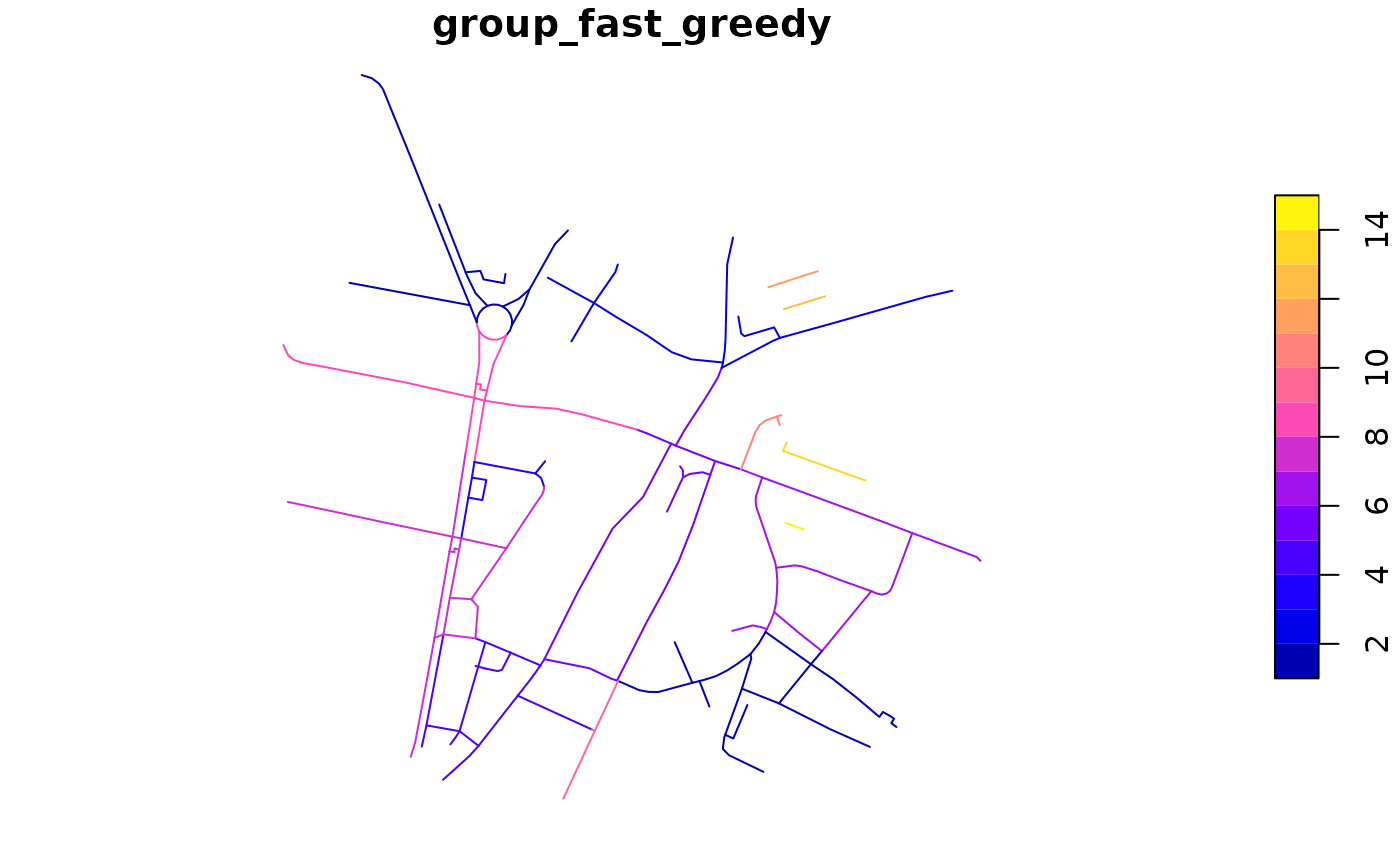
rnet$group <- rnet_group(rnet)
plot(rnet["group"])
# mapview::mapview(rnet["group"])
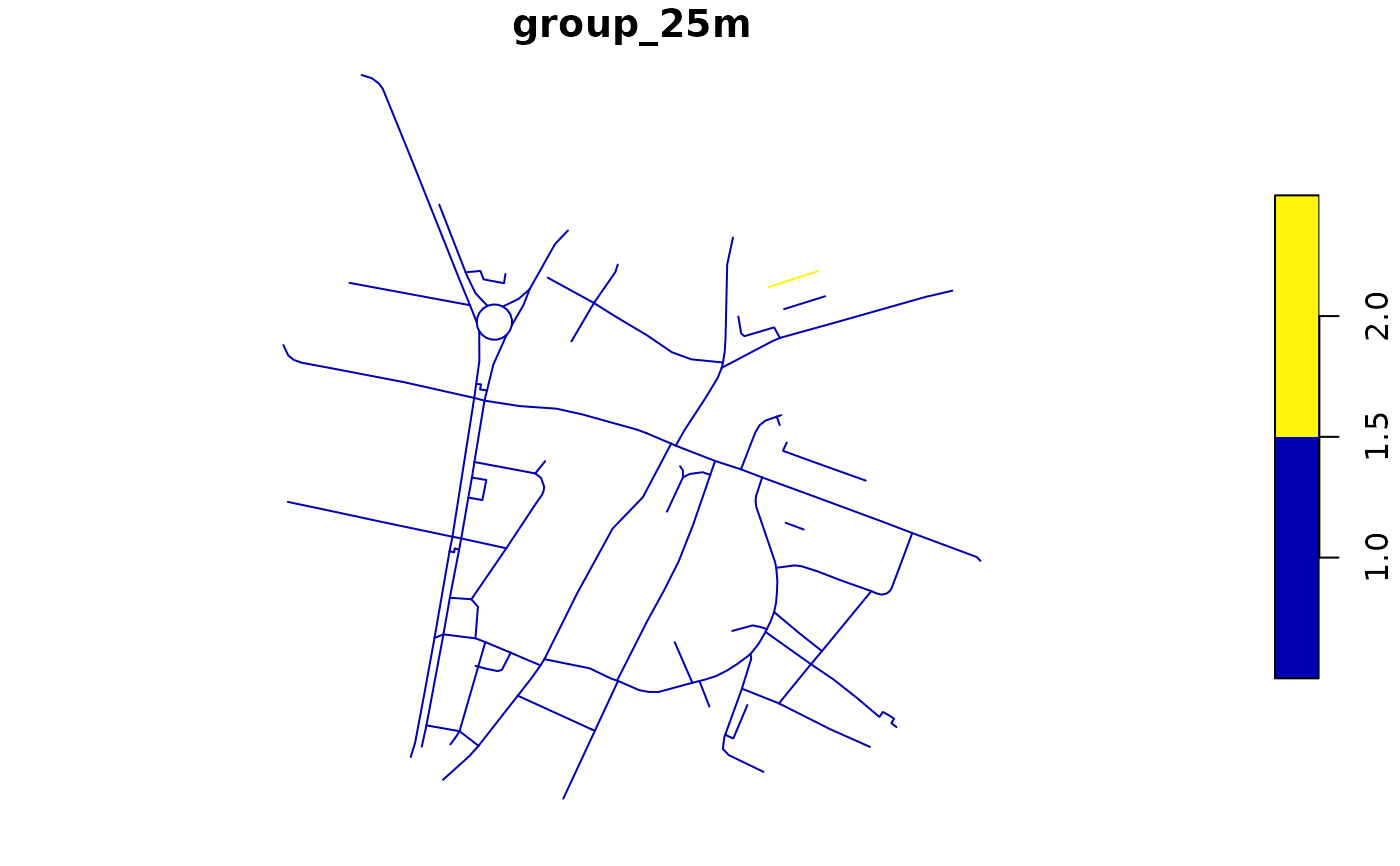
rnet$group_25m <- rnet_group(rnet, d = 25)
plot(rnet["group_25m"])
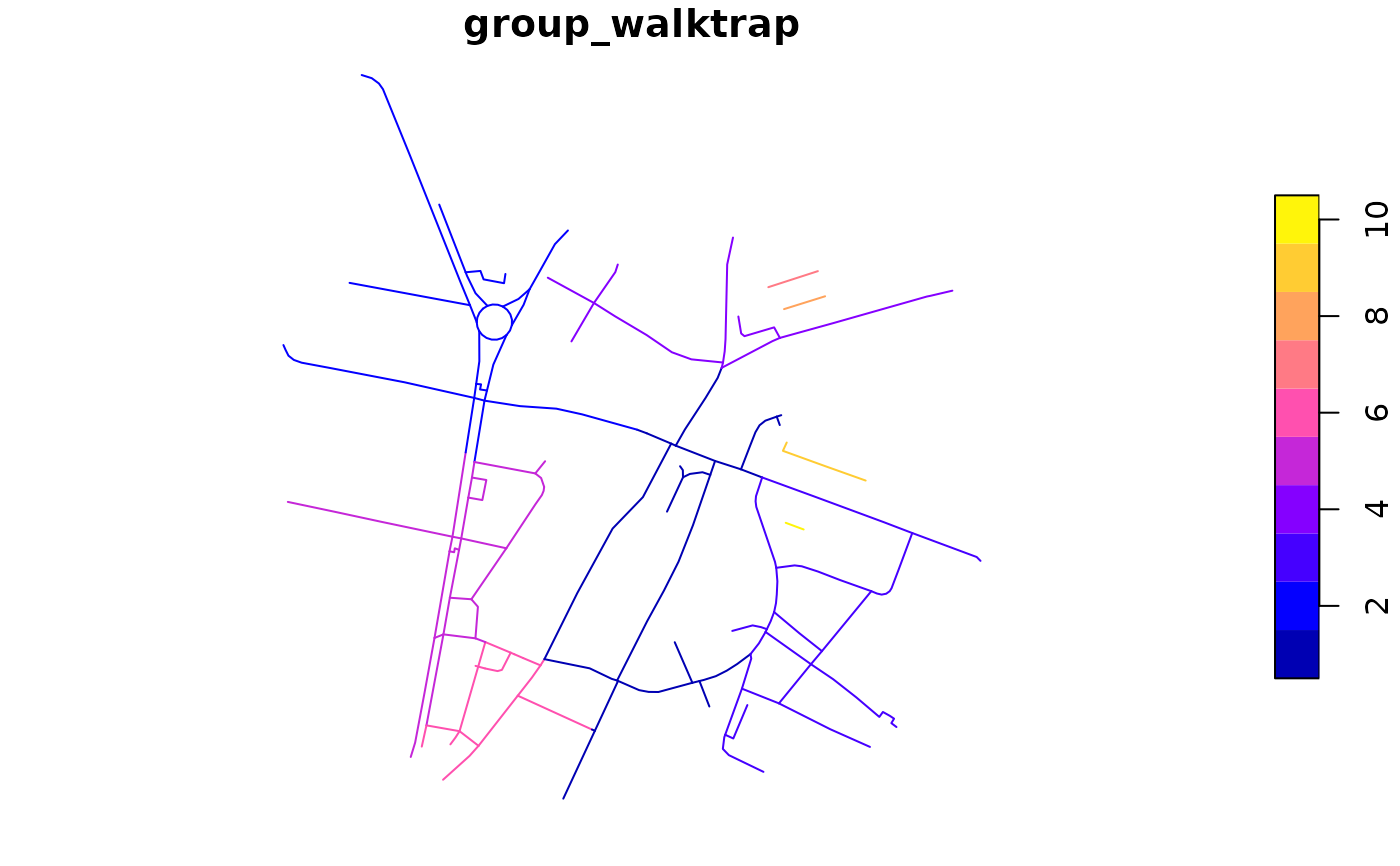
rnet$group_walktrap <- rnet_group(rnet, igraph::cluster_walktrap)
plot(rnet["group_walktrap"])
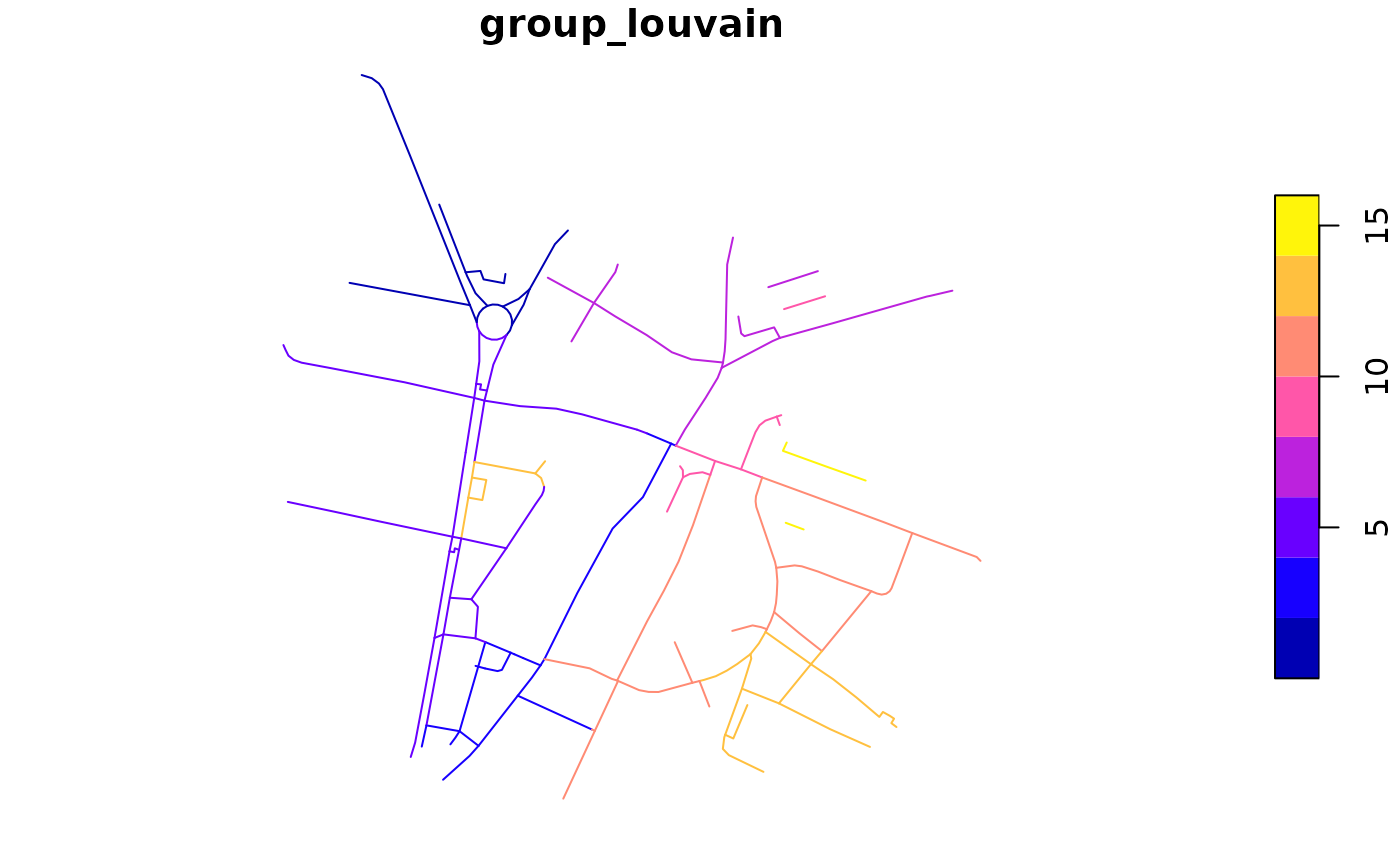
rnet$group_louvain <- rnet_group(rnet, igraph::cluster_louvain)
plot(rnet["group_louvain"])
rnet$group_fast_greedy <- rnet_group(rnet, igraph::cluster_fast_greedy)
plot(rnet["group_fast_greedy"])
}