
weathercan and tidyhydat
Steffi LaZerte
2025-07-25
Source:vignettes/articles/tidyhydat.Rmd
tidyhydat.Rmdtidyhydat is
another R package for accessing data from ECCC. In this case,
tidyhydat gives access to the National
Water Data Archive (HYDAT).
HYDAT contains lots of data including stream flow (historical and real-time), water levels, station metrics and information on data types and codes.
Here we’ll go through a brief example of how hydrology data from
tidyhydat can compliment weather data from
weathercan (and vice versa).
Exploring climate and hydrology
In the summer of 2020, my region (Brandon, Manitoba) experienced an incredibly heavy rain fall event. Our downspout was ripped off the gutter and many people in the area experienced flooding as rain poured into their basements.
Let’s take a look at how this event was captured by weather and hydrometric stations monitored by ECCC.
The event occurred in late June/early July, so let’s give ourselves a two-month range.
dates <- c("2020-06-01", "2020-08-01")We’ll find a local Brandon weather station that has daily data for this range
stations_search("brandon", interval = "day",
starts_latest = 2020, ends_earliest = 2020)## # A tibble: 2 × 17
## prov station_name station_id climate_id WMO_id TC_id lat lon elev tz interval start end normals
## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <lgl>
## 1 MB BRANDON A 50821 5010481 71140 YBR 49.9 -100.0 409. Etc/GMT+6 day 2012 2025 FALSE
## 2 MB BRANDON RCS 49909 5010490 71136 PBO 49.9 -100.0 409. Etc/GMT+6 day 2012 2025 FALSE
## # ℹ 3 more variables: normals_1991_2020 <lgl>, normals_1981_2010 <lgl>, normals_1971_2000 <lgl>In this case “A” is for “Airport”, let’s go with that!
rain <- weather_dl(station_ids = 50821, interval = "day", start = dates[1], end = dates[2])Take a quick look:
ggplot(data = rain, aes(x = date, y = total_rain)) +
theme_bw() +
geom_bar(stat = "identity") +
scale_y_continuous(name = "Total Rain (mm)", expand = c(0,0))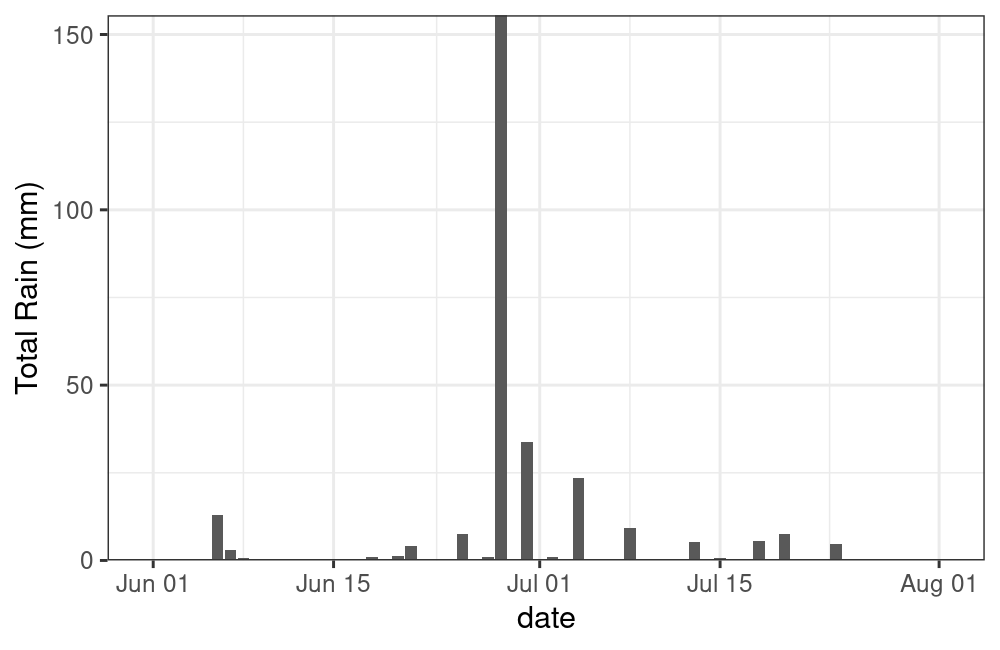
plot of chunk unnamed-chunk-7
Yikes! You can see why my downspout came off!
Now let’s get some HYDAT data to compare. First we’ll find a local station
search_stn_name("brandon")## Error in search_stn_name("brandon"): could not find function "search_stn_name"There are a couple of options, but whoops, one’s from Quebec! Let’s
filter this to only Manitoba and only stations with 2020 data with the
hy_stn_data_range() function.
search_stn_name("brandon") %>%
filter(PROV_TERR_STATE_LOC == "MB") %>%
pull(STATION_NUMBER) %>%
hy_stn_data_range() %>%
filter(Year_from <= 2020, Year_to >= 2020)## Error in hy_stn_data_range(.): could not find function "hy_stn_data_range"Hmm, let’s see what kind of data is available by looking at the
included hy_data_types data frame.
## Error: object 'hy_data_types' not foundGreat! We have both flow and water level data for a station number “05MH001”, “Assiniboine River at Brandon”.
Let’s grab the flow and water level data for this station.
flow <- hy_daily_flows(station_number = "05MH001",
start_date = dates[1], end_date = dates[2])## Error in hy_daily_flows(station_number = "05MH001", start_date = dates[1], : could not find function "hy_daily_flows"
level <- hy_daily_levels(station_number = "05MH001",
start_date = dates[1], end_date = dates[2])## Error in hy_daily_levels(station_number = "05MH001", start_date = dates[1], : could not find function "hy_daily_levels"Ploting rain and flow
g <- ggplot() +
theme_bw() +
theme(axis.title.x = element_blank()) +
geom_bar(data = rain, aes(x = date, y = (total_rain * 2)), stat = "identity",
alpha = 0.7, fill = "cornflowerblue") +
geom_line(data = flow, aes(x = Date, y = Value)) +
scale_y_continuous(name = bquote(Total~Flow~(m^3/s)), expand = c(0, 0),
limits = c(0, max(flow$Value * 1.1)),
sec.axis = sec_axis(transform = ~ . / 2, name = "Total Rain (mm)"))## Error: object 'flow' not found
g## Error: object 'g' not foundInteresting, looks like there’s a bit of a lag between the rain event and the dramatic increase in water flow in the Assiniboine (unsurprisingly, this is called “lag to peak”).
Let’s add a bit of information about this lag to peak.
d <- data.frame(dates = c(rain$date[which.max(rain$total_precip)],
flow$Date[which.max(flow$Value)]),
y = max(flow$Value) + 5)## Error: object 'flow' not found
g +
geom_path(data = d, aes(x = dates, y = y),
arrow = arrow(length = unit(0.25, "lines"), ends = "both", type = "closed")) +
annotate(geom = "text",
x = d$dates[1] + (d$dates[2] - d$dates[1])/2,
y = d$y[1] + 10,
label = glue("{d$dates[2] - d$dates[1]}-day delay"))## Error: object 'g' not foundWe can expect a lag like this because much of the flow being captured by the Brandon HYDAT station is from precipitation in the upstream catchment area (not only from local contributions), which takes time to travel.
Ploting rain and water level
g <- ggplot() +
theme_bw() +
theme(axis.title.x = element_blank()) +
geom_bar(data = rain,
aes(x = date, y = (total_rain/65) + min(level$Value)),
stat = "identity", alpha = 0.7, fill = "cornflowerblue") +
geom_line(data = level, aes(x = Date, y = Value)) +
scale_y_continuous(name = "Water Level (m)", expand = c(0, 0),
sec.axis = sec_axis(transform = ~ (. - min(level$Value)) * 65,
name = "Total Rain (mm)")) +
coord_cartesian(ylim = c(min(level$Value), max(level$Value)*1.001))## Error: object 'level' not found
g## Error: object 'g' not foundAgain there looks to be a lag, let’s see if it’s the same as before.
d <- data.frame(dates = c(rain$date[which.max(rain$total_precip)],
level$Date[which.max(level$Value)]),
y = max(level$Value)*1.00025)## Error: object 'level' not found
g +
geom_path(data = d, aes(x = dates, y = y),
arrow = arrow(length = unit(0.25, "lines"), ends = "both", type = "closed")) +
annotate(geom = "text",
x = d$dates[1] + (d$dates[2] - d$dates[1])/2,
y = d$y[1] * 1.0002,
label = glue("{d$dates[2] - d$dates[1]}-day delay"))## Error: object 'g' not foundPloting flow and water level
Looks like the flow and water level match up, perhaps we should take a closer look.
ggplot() +
theme_bw() +
theme(legend.position.inside = c(0.8, 0.8)) +
geom_line(data = flow, aes(x = Date, y = Value, colour = "Flow"),
linewidth = 2) +
geom_line(data = level, linewidth = 1,
aes(x = Date, y = (Value - min(Value) + 0.1) * 130, colour = "Level")) +
scale_y_continuous(bquote(Total~Flow~(m^3/s)), expand = c(0, 0),
sec.axis = sec_axis(transform = ~ ./130 + min(level$Value) - 0.1,
name = "Water Level (m)")) +
scale_colour_manual(name = "Type",
values = c("Flow" = "cornflowerblue",
"Level" = "grey30"))## Error: object 'flow' not foundAlmost a perfect match between water level and flow (which makes sense).
Hopefully this short article gives you a sense of how you might combine different types of ECCC data gathered via different R packages for a more comprehensive look at the world around.